
When it comes to internal combustion engines, petrol and diesel engines are the two most common types powering vehicles and machines around the world. While both serve the same basic purpose — converting chemical energy from fuel into mechanical power — they operate on different principles, use different fuels, and have distinct characteristics in terms of performance, efficiency, and maintenance.
Working Principle
The primary difference between petrol and diesel engines lies in their working principle. Petrol engines, also known as spark-ignition engines, use a spark plug to ignite a mixture of air and fuel. In contrast, diesel engines, also known as compression-ignition engines, rely on the heat generated by compressing air to ignite the fuel.
Petrol Engine Working
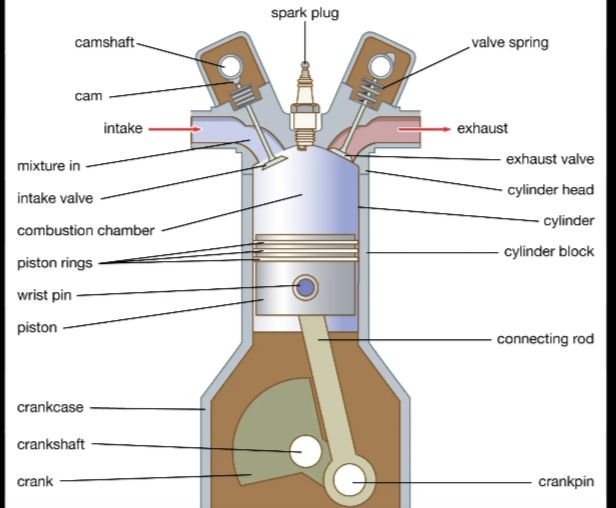
A petrol engine works on the Otto cycle, which consists of four stages:
- Intake Stroke: Air and fuel mixture enters the engine cylinder.
- Compression Stroke: The air-fuel mixture is compressed.
- Power Stroke: The spark plug ignites the mixture, causing combustion.
- Exhaust Stroke: The exhaust gases are released.
Diesel Engine Working
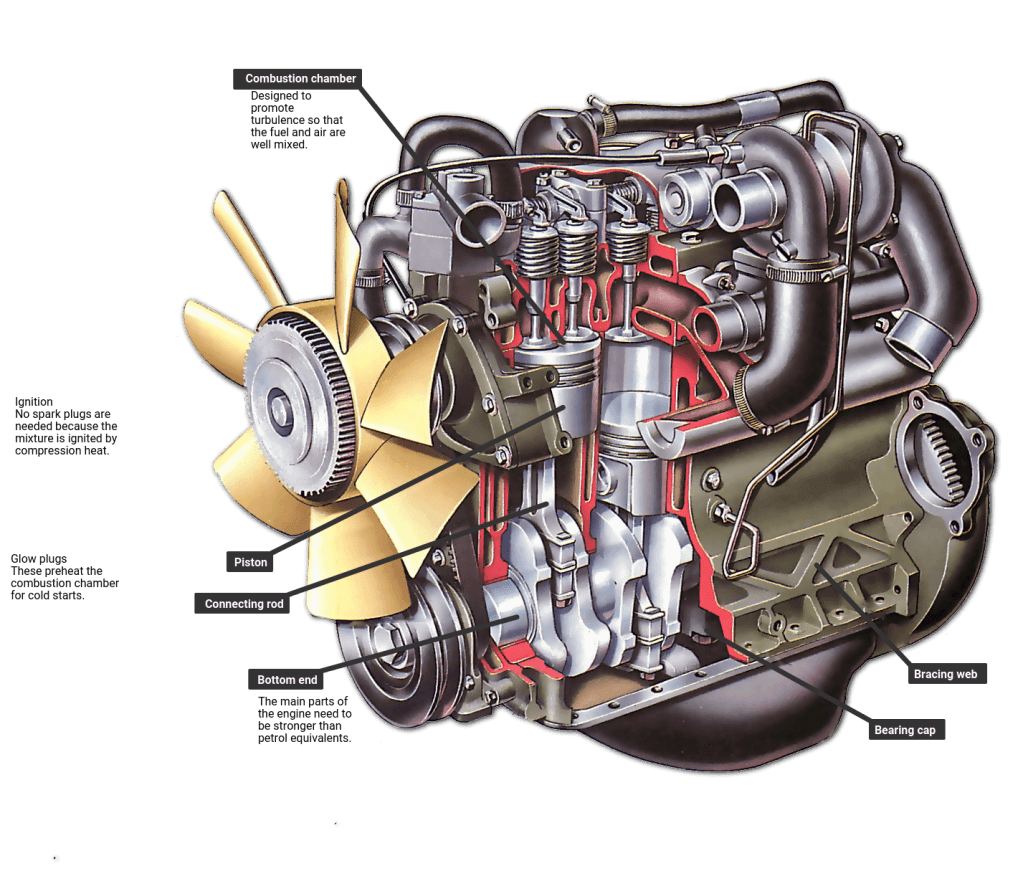
A diesel engine works on the diesel cycle, which also consists of four stages:
- Intake Stroke: Only air enters the engine cylinder.
- Compression Stroke: The air is compressed to a high pressure and temperature.
- Power Stroke: Fuel is injected into the cylinder and ignites due to the heat of compressed air.
- Exhaust Stroke: The exhaust gases are released.
Key Differences
Here are some key differences between petrol and diesel engines:
- Compression Ratio: Diesel engines have a higher compression ratio (14:1 to 25:1) compared to petrol engines (8:1 to 12:1).
- Fuel Efficiency: Diesel engines are more fuel-efficient due to their higher compression ratio and energy density of diesel fuel.
- Torque and Power: Diesel engines produce more torque at lower RPMs, while petrol engines produce more power at higher RPMs.
- Engine Life: Diesel engines generally last longer due to their robust construction and lower RPM operation.
- Maintenance: Petrol engines require less frequent maintenance and are generally less expensive to repair.
Applications
Petrol engines are commonly used in:
- Lightweight vehicles, such as cars and motorcycles
- Smaller engines, such as those used in generators and lawn mowers
Diesel engines are commonly used in:
- Heavy-duty vehicles, such as trucks and buses
- Industrial machinery, such as generators and pumps
- Long-distance hauling and towing applications
Conclusion
In conclusion, petrol and diesel engines have distinct differences in terms of their working principle, design, and applications. Understanding these differences is essential for choosing the right engine for your needs and ensuring optimal performance, efficiency, and maintenance. While petrol engines are suitable for lightweight vehicles and shorter distances, diesel engines are better suited for heavy-duty applications and long-distance hauling .

💬 COMMENT