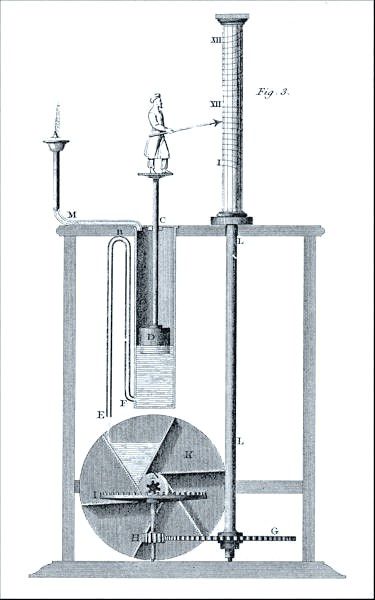
Step into the world of ancient Rome, where time was literally measured drop by drop. The device in the image is a beautifully illustrated example of a Roman water clock, also known by its Greek name, the clepsydra—meaning “water thief.” Unlike sundials, these ingenious clocks worked day and night, rain or shine, making them a groundbreaking solution for timekeeping in an era when precision was rare.
But don’t let its simplicity fool you—this wasn’t just a bucket with a hole. The clepsydra was a masterpiece of engineering, blending Greek innovation (thank you, Ctesibius of Alexandria) with Roman practicality.
key features and why it was such a big deal.
How It Worked: The Secrets of the Clepsydra
1. Regulated Water Flow: The Heart of Precision
Early water clocks had a glaring flaw: as water levels dropped, the flow slowed, making timekeeping unreliable. The Romans and Greeks fixed this with a genius solution—a constant-level reservoir:
– The Reservoir: The tall vertical vessel you see in the drawing wasn’t just for show. It was continuously supplied with water, and an overflow system kept its level steady, ensuring consistent pressure.
– The Steady Flow: This constant pressure meant water flowed out at a uniform rate, solving the problem of uneven hours. It was engineering brilliance in its purest form.
2. Measuring Time with Style
Once the water flowed steadily, it entered the main chamber, where the magic of time measurement happened:
– The Float Mechanism: As water filled the chamber, a float (possibly that square block with the vertical rod) rose with it.
– The Indicator: The float’s movement was linked to a rod with a figure on top. As the float rose, the figure pointed to markings or scales on the column, showing the hour of the day or night.
This wasn’t just functional—it was mesmerizing to watch!
3. Advanced Gearing: Turning Time into a Spectacle
Some of the most sophisticated clepsydrae didn’t stop at simple time measurement. They turned timekeeping into an art form, using gears and mechanisms to create dramatic displays:
– Rotating Hour Dials: Gears driven by the float could turn cylinders or dials marked with the hours.
– Seasonal Adjustments: Advanced designs even accounted for the fact that “hours” weren’t always the same length—longer in summer, shorter in winter.
– Automata and Bells: The gears could also power automata (mechanical figures) that struck bells or announced the hour, making the clepsydra not just a clock but a public spectacle of Roman ingenuity.
Why It Mattered: The Role of Water Clocks in Roman Life
The clepsydra wasn’t just a fancy gadget—it was a crucial part of daily life in ancient Rome:
– In the Courts: Water clocks were used to time legal speeches, ensuring fairness by limiting how long someone could argue. Imagine a lawyer running out of time as the last drop fell!
– In the Military: Night-watch shifts were regulated using clepsydrae, keeping soldiers on schedule even in the dead of night.
– A Symbol of Genius: These clocks were engineering marvels, combining practicality with sophistication. In fact, Ctesibius’s designs were so precise they remained unmatched for nearly 1,800 years—until the invention of the pendulum clock in the 17th century.
Why It Still Inspires Us Today
The Roman water clock wasn’t just a tool; it was a testament to human ingenuity. It showed how curiosity and creativity could turn something as simple as dripping water into a reliable, complex, and even artistic way to measure time. It’s no exaggeration to say that the clepsydra was one of the most advanced mechanical devices of the ancient world, and its legacy still flows through the veins of modern engineering.
So next time you check the time on your watch or phone, take a moment to appreciate the drop-by-drop brilliance of the clepsydra—the “water thief” that stole the spotlight in ancient Rome!

💬 COMMENT